According to Dr. Russell Barkley, a top ADHD expert, children with ADHD generally fall behind with their peers by 30% in this area. In this scenario, a lower mental age indicates disparities in cognitive development rather than a lack of intelligence or potential.
This may include differences in functions like the skills we use to focus, remember instructions, plan, and juggle multiple tasks. These skills include working memory, emotional control, and emotional maturity.
In this article, we’ll walk you through how to interpret the ADHD mental age chart, how it can be useful for both children and adults, and what its limitations are.
What is the ADHD Mental Age Chart?
The ADHD Mental Age Chart is a tool for understanding how children and people with ADHD develop emotional and cognitive abilities at different rates than their peers. According to the 30% rule, persons with ADHD are typically 30% behind their chronological age in terms of executive function and emotional development.
For example, a 10-year-old with ADHD may have the emotional maturity of a 7-year-old. This chart assists parents, educators, and people in recognising developmental variances and providing appropriate support based on their specific requirements.
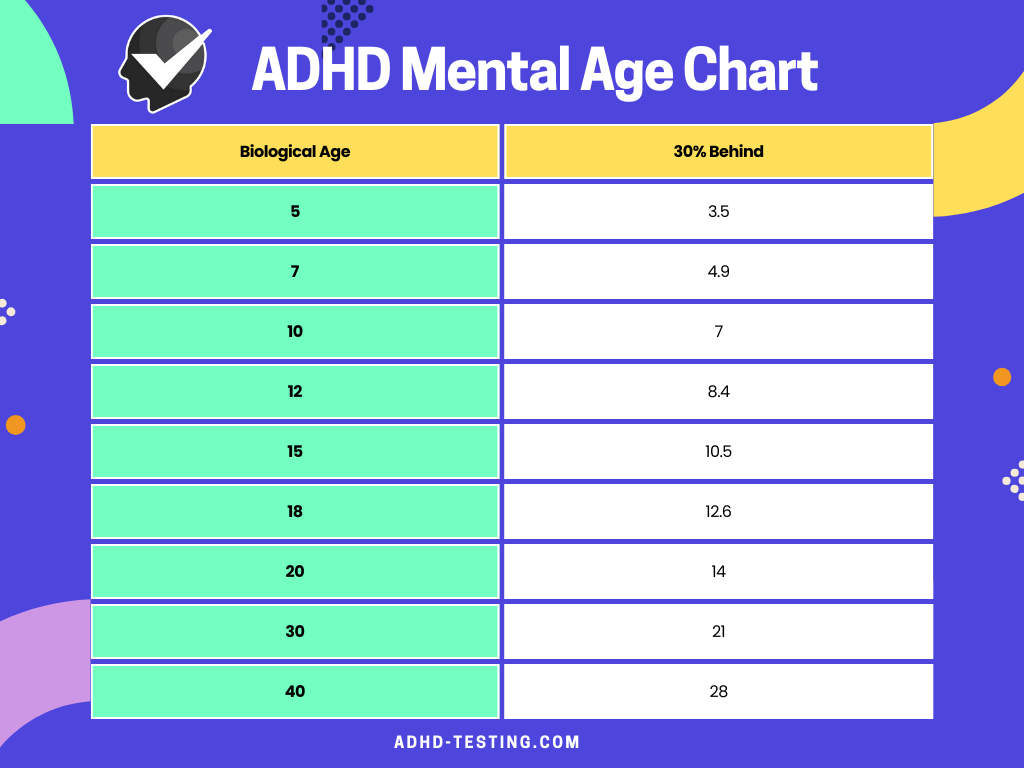
How to Interpret the ADHD Mental Age Chart
The 30% rule in ADHD refers to the idea that people with ADHD may have a 30% delay in different aspects of their development when compared to their peers who are not diagnosed with ADHD. This rule is not a rigorous scientific law, but rather a guideline for understanding the developmental obstacles that people with ADHD frequently go through.
A mental age chart often contrasts several elements of cognitive and emotional performance with age-appropriate norms. These charts also suggests that, even though people with ADHD are chronologically in their 30s or 40s, their executive functioning abilities (such as organisation, time management, and impulse control) are more similar to those of a younger person.
Interpreting mental age charts for ADHD adults needs an extensive knowledge of both ADHD and developmental psychology. Remember, these charts aren’t intended to infantilise people who have ADHD or imply that they’re less capable overall. Instead, they give a framework for identifying particular areas where additional help or efforts may be useful.
Using the ADHD Mental Age Chart for Child Development
Your child’s executive dysfunction may impair their problem-solving abilities, attentional control, and the rate at which they learn new information. Adults with ADHD must be patient with themselves since our brains simply function differently.
Here’s a brief look at how executive function can affect people with ADHD as they age, keeping the ADHD 30% rule in mind:
1. Baseline or Pre-Executive Function Stage (Age 0-2): Toddlers develop fundamental self-control and awareness. Transitions can be more difficult for a kid with ADHD symptoms, and tantrums may occur more frequently. They’re still learning, but at their own speed.
2. Instrumental or Self-Directed Abilities Stage (Age 2-6): Children start to learn self-control and basic instructions. Halfway through an activity, children with ADHD may become sidetracked or forget what they were supposed to perform.
3. Methodical or Self-Reliant Abilities Stage (Age 6-11): Kids begin to make plans and think ahead. A child with ADHD may become distracted or fail to complete their assignments.
4. Tactical or Reciprocal Abilities Stage (Age 9-13): Children begin to comprehend the viewpoints of others. Impulsivity and considering other people’s perspectives can be difficult for a child with ADHD.
5. Strategic or Cooperative Abilities Stage (Age 14-21): Young adults set long-term goals and make plans. A person with ADHD might struggle with long-term planning or get overwhelmed by complex tasks.
With this understanding, you can better help your child navigate their world. This will improve their confidence and overall mental health. Here are some strategies to get you started:
- Explain ADHD and mental age differences positively: Without assigning labels, help your kid comprehend ADHD and how it affects development. Remember to always praising their abilities and skills, steering away from feelings of inferiority.
- Develop predictable routines: Children who have clear timetables are less stressed and are better able to anticipate everyday responsibilities. Establish regular schedules for homework, meals, and bedtimes while allowing flexibility when needed.
- Break down big tasks into smaller ones: Choose a task and give it your whole attention by setting a timer for 25 minutes. Write down irrelevant ideas for later while working without interruptions. You may pause for 5 to 10 minutes to refuel when the timer goes off. Continue the cycle, and reward yourself with a longer rest of 30-60 minutes after 4 sessions.
- Encourage physical activities: Find out what your child enjoys and is good at, like music, athletics, or painting. They can gain confidence and find a way to release their energy by participating in activities they like.
Above everything, be kind, patient, and supportive. They will become more proficient at using their executive functions as they mature.
Applying the ADHD Mental Age Chart to Adults
Just like with children, the 30% rule of the ADHD mental age chart affects various aspects of life for ADHD adults. Some of them include:
- Time management: An adult with ADHD may have trouble managing their time as well as a person who is 30% younger.
- Emotional Control: A younger person’s emotional reactions could be more appropriate.
- Organising Skills: Considering their age, their organisational abilities may be below average.
- Career Development: It might take longer or be harder to advance professionally.
- Relationships: Developmental differences may cause problems in romantic and social relationships.
If we put the ADHD mental age chart into effect, consider 28-year-old content creator Alex, who has ADHD. According to his mental age chart, his organisational abilities are more in line with those of a 20-year-old, even though his creative thinking corresponds with his chronological age. Alex and his company collaborate to put personalised plans into place that maximise his creativity and increase his output by applying the 30% rule.
How To Manage Hyperactivity in ADHD
For people with ADHD and a range of mental ages, several forms of therapy can be helpful, such as:
1. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT):
By identifying and addressing dysfunctional thought processes, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) aims to regulate the symptoms of attention. People with higher mental ages may benefit from it by developing their executive functioning, problem-solving abilities, and self-awareness.
CBT improves self-esteem, controls emotions, and supports the growth of cognitive abilities in individuals with younger mental ages.
2. Social Skills Training:
Regardless of their mental age, people with ADHD may benefit from social skills training. It focusses on enhancing one’s ability to solve problems, develop relationships, and communicate effectively. People who are intellectually older may find this useful in establishing enduring connections and managing social difficulties.
People with lower mental ages can benefit from social skills training by strengthening their peer interactions and developing age-appropriate social skills.
3. Parent Education and Training:
Parents of children with ADHD may benefit greatly from parent education and training programs. These sessions address managing symptoms of ADHD, improving social relationships, and creating a safe but supportive environment. With the correct knowledge and tools, parents can effectively control their child’s ADHD symptoms and support their cognitive development.
It is important to remember that mental age is not a measure of potential or intelligence, but rather a tool for better understanding how someone functions cognitively. If given the right support, accommodations, and techniques, people with ADHD may flourish and overcome the challenges posed by ADHD.
By embracing their unique abilities and attending to their demands, people with ADHD can surely have successful, fulfilling lives and reach their full potential.
Frequency-Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions that our experts have addressed regarding the ADHD mental age chart:
What is the mental age of someone with ADHD?
Up until the age of 35, the frontal lobes of the brain—which are implicated in ADHD—continue to develop. Practically speaking, this implies that individuals with ADHD should anticipate a gradual reduction in their symptoms. It takes many people until their late 30s to reach the emotional maturity of a 21-year-old.
What is a mental age chart?
One technique for assessing a person’s cognitive ability according to their age is a mental age chart. It assesses whether a person is developing at a normal pace by comparing their mental age to their chronological age.
What age is ADHD hardest?
Hyperactivity symptoms are often most intense between the ages of 7 and 8, and then gradually decrease as you age. However, there is no age at which inattentive conduct reaches its maximal intensity.
What age does ADHD calm down?
Symptoms of hyperactivity in ADHD normally decrease in late childhood and early adolescence.
What are some other assessments used to diagnose ADHD?
Other assessments used to diagnose ADHD include behavioral assessments, rating scales, and neuropsychological testing. These assessments look at a person’s behavior, attention, and cognitive abilities to determine if they meet the criteria for ADHD.














